US States Map
- Alabama Map
- Alaska Map
- Arizona Map
- Arkansas Map
- California Map
- Colorado Map
- Connecticut Map
- Delaware Map
- Florida Map
- Georgia Map
- Hawaii Map
- Idaho Map
- Illinois Map
- Indiana Map
- Iowa Map
- Kansas Map
- Kentucky Map
- Louisiana Map
- Maine Map
- Maryland Map
- Massachusetts Map
- Michigan Map
- Minnesota Map
- Mississippi Map
- Missouri Map
- Montana Map
- Nebraska Map
- Nevada Map
- New Hampshire Map
- New Jersey Map
- New Mexico Map
- New York Map
- North Carolina Map
- North Dakota Map
- Ohio Map
- Oklahoma Map
- Oregon Map
- Pennsylvania Map
- Rhode Island Map
- South Carolina Map
- South Dakota Map
- Tennessee Map
- Texas Map
- Utah Map
- Vermont Map
- Virginia Map
- Washington Map
- West Virginia Map
- Wisconsin Map
- Wyoming Map
West Virginia Map
West Virginia, constituent condition of the United States of America. Owned up to the association as the 35th state in 1863, it is a somewhat little state.
West Virginia State Map
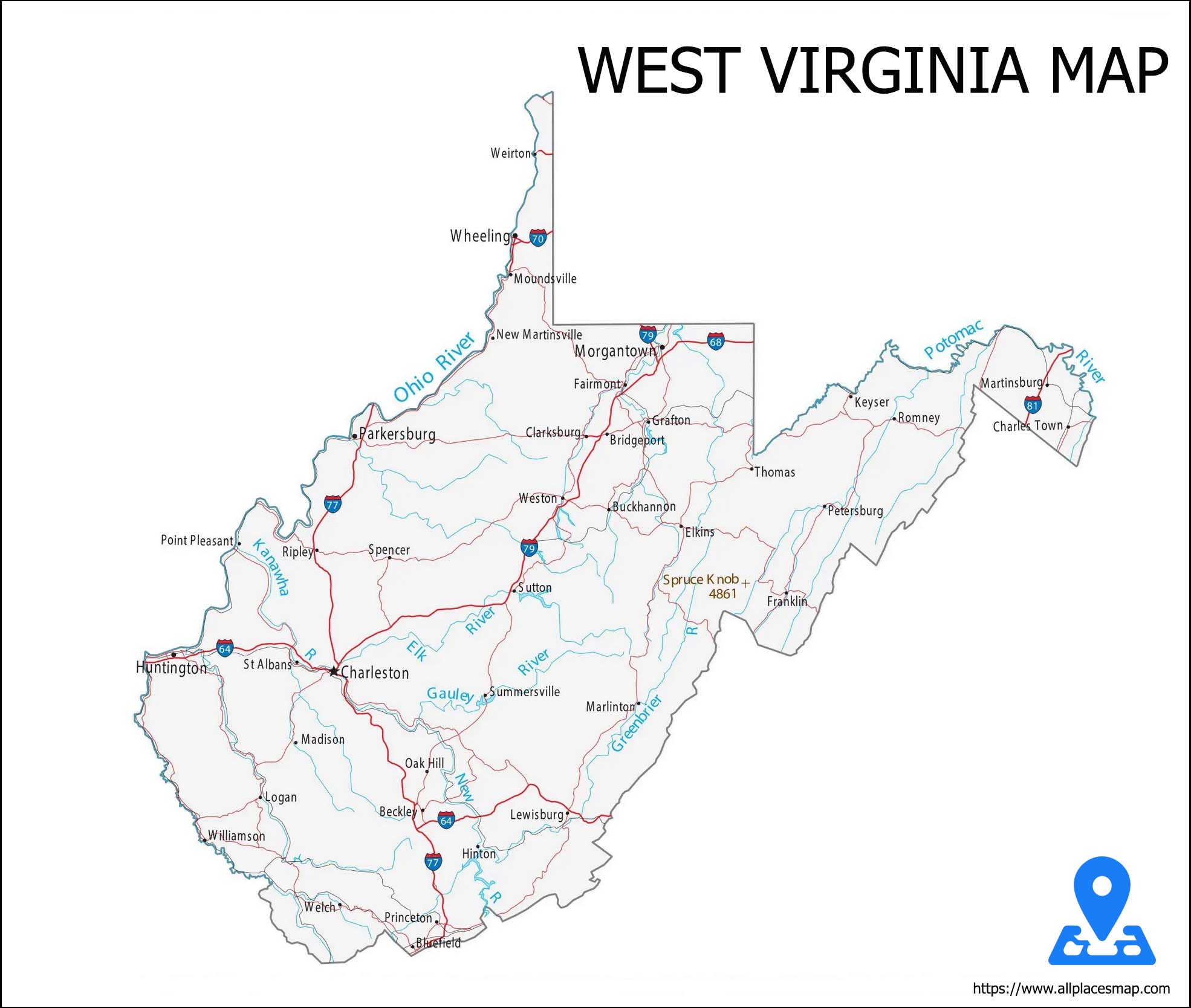
It is lined by Pennsylvania toward the north, Maryland and Virginia toward the east,
West Virginia legitimizes all around its moniker, the Mountain State. With a normal rise of around 1,500 feet (460 meters) above ocean level, it is the most noteworthy of any U.S. state east of the Mississippi River. It is a locale tied financially and socially to the mountain spines that range length and broadness and to the waterways wall it in on many sides. Initially it established the northwestern part of Virginia, however its occupants resisted the state's withdrawal show in 1861, picking rather to stay inside the association. After two years the region framed another express, its populace acting much in the practice proposed by the maxim of West Virginia, "Montani semper liberi" ("Mountaineers are free all the time").
Land region in West Virginia
The most extreme rise in West Virginia is 4,863 feet (1,482 meters) at Spruce Knob, in the east. The absolute bottom is 247 feet (75 meters) at Harpers Ferry, situated on a precarious tongue of land transcending the conjunction of the Shenandoah and Potomac streams. The land is rough, going from sloping to precipitous, and there are no broad spreads of level land. The state has two begs, one cutting toward the north among Pennsylvania and Ohio, the other toward the east among Maryland and Virginia.
All of West Virginia is a piece of the Appalachian Mountain framework. It is regularly partitioned into two significant physiographic districts: the Appalachian Plateau Province and the Ridge and Valley Province. By and large, these are isolated by the Allegheny Front, separating the waters that stream to the Atlantic Ocean from those streaming to the Gulf of Mexico. The Appalachian Plateau Province covers the western 66% of the state and agrees with the Ohio River seepage bowl. It is an area seriously took apart by streams into a labyrinth of slopes and valleys, and, in places, the first level surface shows as the uniform high levels of the leftover reaches. The eastern piece of the level, with the most noteworthy heaps of the state, is alluded to as the Allegheny Mountain area. The Allegheny Mountains incorporate in excess of 40 tops more than 4,000 feet (1,200 meters) in height, prompting weighty precipitation nearby and making it the wettest in the state and the wellspring of a considerable lot of its waterways. The eastern edge of the state and the eastern beg involve the Ridge and Valley Province. This geologic territory takes in a large portion of the Potomac River bowl and is popular for its upper east southwest collapsed mountain arrangement, a piece of the chain coming to from Canada to north-focal Alabama. The northern finish of the Blue Ridge Mountains frames a minor district in the easternmost finish of the eastern beg.
Streams and soils in West Virginia
The seepage east of the Allegheny Front elements a trellised design streaming toward the upper east and at last depleting into the Potomac. The western parts channel across a slanted plane by a more extended, dendritic seepage design that streams commonly northwest into the Ohio River. A tiny region channels into the heading out east James River arrangement of Virginia.
Seepage over West Virginia's tough surface has made a portion of the state's most useful and level alluvial soils on the bigger waterway floodplains. The endured limestone soils of the east are appropriate for field and plantations. A portion of the dirt soils along the Ohio River are bases for the pottery business. As a general rule, notwithstanding, the high alleviation and deciduous timberland of the Appalachian Plateau Province produce a slender, rough, acidic soil not helpful for huge scope business cultivating.
Environment of West Virginia
The state has particular times of about equivalent length. It has a muggy mainland environment aside from a marine adjustment in the eastern beg. Mean yearly temperatures, reflecting scope and rise, range from around 56 °F (13 °C) in the south to 52 °F (11 °C) in the north and 48 °F (9 °C) in the most precipitous locales. January is the coldest month, with a statewide normal of 33 °F (1 °C), and July is hottest, with a 73 °F (23 °C) normal. The developing season midpoints 160 days yet goes from 120 to 180 days. West Virginia lies in the scope zone of the westerly breezes, so most tempest tracks, fronts, and wind heading come from the northwest, west, or southwest. Mean yearly precipitation differs from more than 60 inches (1,520 mm) in the rugged regions to 35 inches (890 mm) in the downpour shadow only east of the mountains. Snowfall, which makes up around 8% of the all out precipitation, differs from an occasional normal of under 20 inches (510 mm) in the southwest to more than 64 inches (1,620 mm) in the eastern mountains.
Find FIPS Codes
Economy of West Virginia
West Virginia has customarily kept a poor monetary situation among the states. Various variables have incited out-movement since World War II. During the 1950s and '60s mine automation and declining coal utilize added to a diminishing interest for work. Rough land and restricted ranch size hampered motorization of agribusiness, and the upper hand moved to states with more level and broad land. Unfamiliar contest in the glass and pottery industry additionally decreased financial open door. Progressively, the absence of level land for modern and business extension likewise has blocked improvement.
In 1965 the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) was laid out as a component of Pres. Lyndon B. Johnson's Great Society program. Appalachia was distinguished as one of the districts in the United States that was seriously slacking in financial turn of events. The ARC has given assets to interstate and transportation improvement to rustic regions and in any case has upgraded nearby framework to draw in financial turn of events. Of the 13 states recognized as a feature of Appalachia, just West Virginia is completely inside the locale.