US States Map
- Alabama Map
- Alaska Map
- Arizona Map
- Arkansas Map
- California Map
- Colorado Map
- Connecticut Map
- Delaware Map
- Florida Map
- Georgia Map
- Hawaii Map
- Idaho Map
- Illinois Map
- Indiana Map
- Iowa Map
- Kansas Map
- Kentucky Map
- Louisiana Map
- Maine Map
- Maryland Map
- Massachusetts Map
- Michigan Map
- Minnesota Map
- Mississippi Map
- Missouri Map
- Montana Map
- Nebraska Map
- Nevada Map
- New Hampshire Map
- New Jersey Map
- New Mexico Map
- New York Map
- North Carolina Map
- North Dakota Map
- Ohio Map
- Oklahoma Map
- Oregon Map
- Pennsylvania Map
- Rhode Island Map
- South Carolina Map
- South Dakota Map
- Tennessee Map
- Texas Map
- Utah Map
- Vermont Map
- Virginia Map
- Washington Map
- West Virginia Map
- Wisconsin Map
- Wyoming Map
Utah Map
Utah, constituent condition of the United States of America. Mountains, high levels, and deserts structure the majority of its scene. The capital, Salt Lake City, is situated in the north-focal locale of the state. The state lies in the core of the West and is limited by Idaho toward the north, Wyoming toward the upper east, Colorado toward the east, Arizona toward the south, and Nevada toward the west. At Four Corners, in the southeast, Utah meets Colorado, New Mexico, and Arizona at right points, the main such gathering of states in the country. Utah turned into the 45th individual from the association on January 4, 1896.
Utah State Map
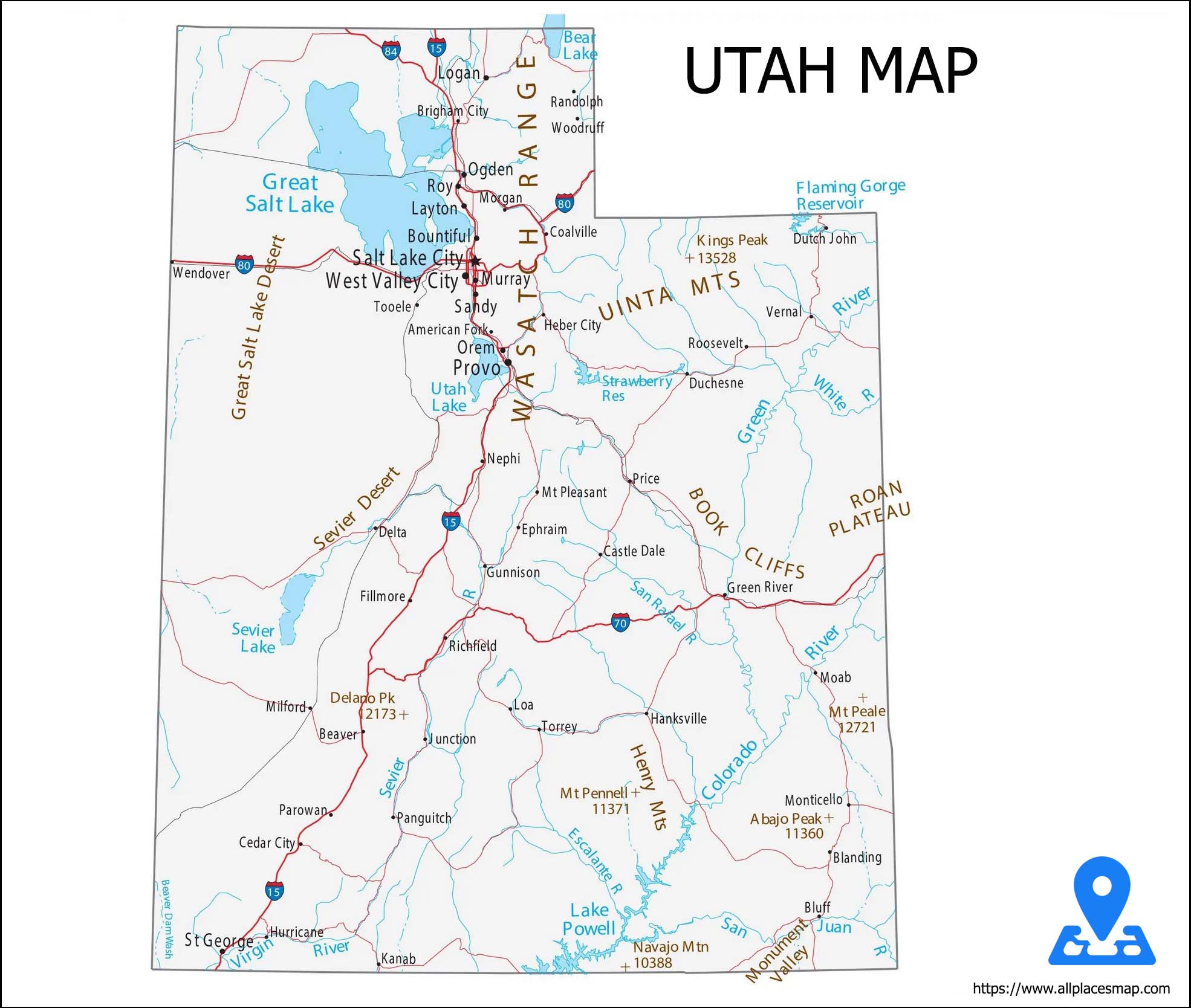
Utah addresses an interesting episode in the settlement of the United States,
Before the appearance of the main Mormon trailblazers, Utah was occupied by a few Native American clans, including the Ute, for whom the state is named. From the start of Mormon settlement in 1847, the trailblazers set about wresting a green land from the deserts, steadily enhancing their harvests with the results of industry and the earth. The economy of present-day Utah depends on assembling, the travel industry, and administrations, notwithstanding horticulture and mining. Region 84,898 square miles (219,884 square km). Populace (2020) 3,271,616.
Seepage in Utah
Utah adds to three significant seepage regions the Colorado and Columbia streams and the Great Basin. The Colorado and its feeder, the Green, channel eastern Utah. The Colorado River Storage Project remembers a few dams and numerous lakes for that area. Streams in the focal and western pieces of the state incorporate the Bear, Weber, Provo, Jordan, and Sevier, all of which stream into the Great Basin. The Raft River and Goose Creek, in the northwestern corner of the state, feed into the Snake River, part of the Columbia River waste. All of the stream frameworks are significant for their water system and power potential.
Water system was among the main Mormon trailblazer endeavors in 1847, and from that point forward water system and water protection have become progressively significant. The water system complex in Utah contains various dams, supplies, waterways and trenches, pipelines, and streaming wells, selective of the enormous Glen Canyon and Flaming Gorge dams. State sheets and offices manage water use, while the division of wellbeing keeps up with water-quality norms under the Water Pollution Control Act of 1953.
During the Pleistocene Epoch (around 2,600,000 to 11,700 quite a while back), the district's colossal Lake Bonneville covered a region as extensive as Lake Michigan. The Great Salt Lake, saline Sevier Lake, and freshwater Utah Lake are the significant leftovers of Lake Bonneville.
Soils in Utah
The desert soil that covers a large portion of the state needs numerous natural materials however contains lime. Absence of satisfactory waste in the Great Basin has harmed encompassing soils with saline materials and antacid salts. The most extravagant soils are in the focal point of the state, from the Idaho line nearly to Arizona, where most cultivating is finished. Mountain soils give a territory to conifers and different trees.
Environment of Utah
Utah's geographic area corresponding to the mountain frameworks of the West, which redirect a significant part of the area's precipitation, makes it fundamentally a bone-dry state. Southwestern Utah, which has a warm, practically dry, subtropical environment, notwithstanding, is alluded to as Utah's "Dixie." The southern piece of the Colorado Plateau has cool, dry winters and wet summers, with regular rainstorms. Northern Utah is impacted via air masses from the northern Pacific Ocean and mainland polar air; it gets a large portion of its precipitation in the cool season.
The state has four particular seasons. The normal temperature in July is in the low 70s F (around 21 °C). In winter the normal temperature is somewhat beneath freezing besides in Dixie. Everyday temperatures fluctuate generally: when Salt Lake City has July highs of 90 °F (32 °C) or above, evening temperatures range from the mid-50s to the mid-60s F (around 13 to 18 °C). Generally low stickiness wins; normal precipitation is around 11 inches (280 mm) a year, changing from under 8 inches (200 mm) over the Great Salt Lake Desert to 50 inches (1,280 mm) in the Wasatch Mountains. The normal yearly snowfall is around 4.5 feet (1.5 meters), going from none in the southwestern valleys to in excess of 10 feet (3 meters) at ski resorts. The normal developing season is 131 days.
Plant and creature life
Around 4,000 plant species fill in Utah's generally fluctuating climatic zones, from the deserts of the southwest, the Great Basin, and the Canyonlands to the tundra of the great mountain tops. In the south are observed creosote shrubbery, mesquite, cactus, yucca, and Joshua tree; the antacid deserts are the environment of shad scale, saltbush, and greasewood. Juniper and sagebrush fill in the lower regions and mountain valleys, as do piñon pine and local grasses. In the mountains develop pines, firs, aspen, and blue tidy. Wood covers around 33% of the state's territory region.
People groups in Utah
The populace is basically all of European family, mostly northern European. There are little extents of Asians, Hispanics, Native Americans, and African Americans. Also, in the late twentieth century, the quantity of Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders expanded; large numbers of them were converts to Mormonism who migrated to Salt Lake City. Aside from Native Americans, almost four-fifths of the minority populace lives in the three Wasatch Front districts of Salt Lake, Davis, and Weber.
Find FIPS Codes
The number of inhabitants in San Juan area is around one-half Native American, containing almost 33% of the state's absolute Native American populace. These are generally Navajo, who dwell fundamentally in the Four Corners area of the Navajo Reservation. The Ute live on the Uintah and Ouray Reservation. Various Southern Paiute, among the most run down of the clans, live on a few little reservations in southern Utah.
Economy of Utah
The early Mormon pioneers, starting in 1847, assembled an independent economy in light of agribusiness, painstaking work, and little industry. With the appearance in the last part of the 1860s of countless different pioneers, this agreeable economy was enhanced by a non-Mormon territory gave to mining, a movement that conflicted with Mormon teaching, and to exchanging. After statehood the exportable assets of the state were taken advantage of to a rising degree by outside organizations and undertakings, and the horticulture of the state moved in the direction of reach steers, fleece, and such business crops as hay (lucerne) and sugar beets. The financial downturns of 1921 and the 1930s were extreme, yet government programs and the government assistance program of the Mormon church assisted the state with recuperating. During World War II a few safeguard plants and air bases were constructed, and southeastern Utah had a uranium blast. In the last part of the 1950s a few enormous plants were raised along the Wasatch Front to fabricate rocket motors for rockets.
The state's economy is exceptionally enhanced. The agrarian and mining areas have been enhanced by light and weighty assembling, money, transportation, and the travel industry. Salt Lake City is a territorial focal point of money and exchange, and many huge undertakings have workplaces there.